The Role of Customer Value Management
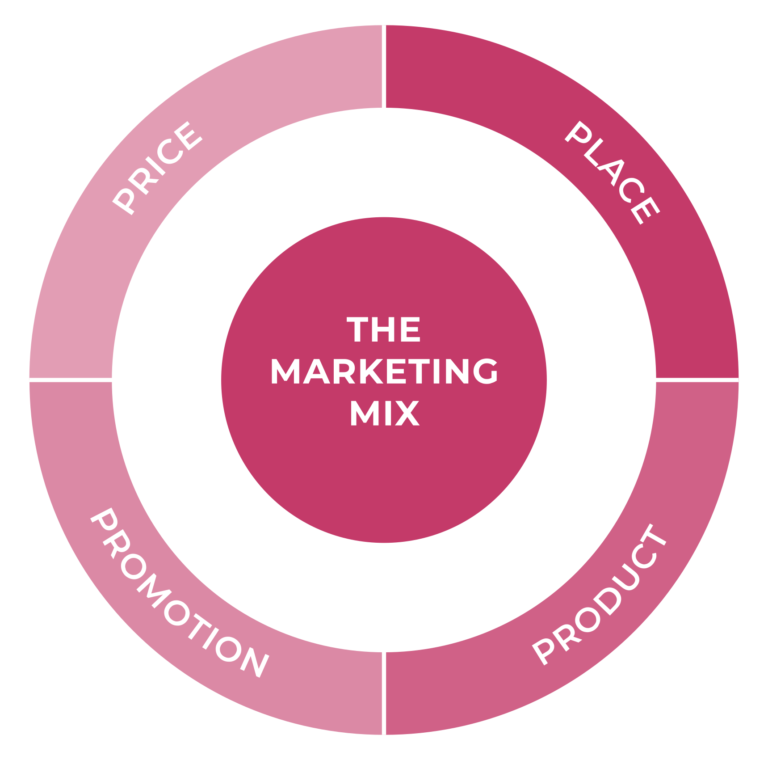
CVM is a part of the broader discipline called marketing. Traditional marketing is grounded in Philip Kotler’s renowned 4Ps framework— product, price, place, and promotion. The 4Ps have long guided businesses in creating offerings, setting prices, distributing products, and stimulating demand (see Figure 2.1).
While this framework provides a solid foundation, it overlooks a crucial element: the customer.
The Transformation from a Product-centric to a Customer-centric Approach
In the beginning of the book we identified that telecoms are uniquely positioned to capitalize on CVM due to their subscription-based business model. Telecoms have:
- Continuous product usage
- Continuous relationships with customers
- The capability to analyze an individual customer’s behaviors and needs
- Ownership of direct communication with customers
Traditional marketing focuses heavily on the 4Ps, emphasizing product features, competitive pricing, distribution channels, and promotional tactics to drive sales. And while effective in generating acquisition, this approach overlooks the unique characteristics of subscription-like products. Organizations that rely on the 4Ps are very product centric—they do not take into account the individual needs and experiences of customers, treating them as mere recipients rather than active participants in the value creation process.
CVM expands the 4P framework by integrating a customer-centric perspective. It balances the focus on products with a deep understanding of customer behaviors, preferences, and their value. For example, instead of promoting the same data plan for everyone, a CVM-driven approach might tailor the offer to specific customer segments by analyzing their actual usage patterns. A heavy data user will receive an offer for unlimited data with added value services, while casual users might be presented with a cost-effective plan with capped data options.
The beauty of CVM is that customer segmentation is limitless, and the ultimate goal is to deliver a true one-to-one communication experience. To achieve this goal, you should not just take a product perspective but also focus deeply on customer needs.
Embracing a customer-centric focus doesn’t mean sidelining focus on business results. Instead, it signifies a shift from a transactional mindset that’s focused on short-term gains (increased one-time sales), to a strategy that seeks greater business impact through long-term relationship-building. This approach emphasizes customer trust, loyalty, and customer advocacy, ultimately leading to sustained profitability.
Embracing Customer Value Principles
To make a customer-centric vision a reality, the CVM team must align the organization with fundamental customer value principles. These principles guide every action and shape how you interact with your customers, especially in customer-facing and product development roles. While each organization may have unique principles based on its strategy and brand promise, two stand out for their importance.
Principle #1: Always Act in the Customer’s Best Interest
The foremost principle is to always act in the customer’s best interest. This means prioritizing the customer’s needs in every interaction. By doing so, you build trust and foster long-term relationships that enhance customer lifetime value (CLV). This principle permeates all aspects of your dealings with customers. For example, you avoid hidden fees and provide clear, straightforward contract terms. You simplify billing statements to make information easy to understand. You tailor offers to meet individual customer needs based on their usage patterns and preferences. You also anticipate customer needs and address potential issues before they escalate.
Principle #2: Always Deliver Value
The second critical principle is to consistently deliver value. You ensure that your products and services meet or exceed customer expectations. Delivering value can take many forms. Sometimes it means helping customers relocate their broadband service smoothly and without excessive charges. Other times it involves assisting customers in adopting new technologies like teaching them how to use the latest smartphone features. It could also be advising customers to upgrade to a larger plan to avoid the higher costs of add-ons and consumption fees even though they might be more profitable in the short term for the company.
By embracing these customer value principles, you move beyond a transactional mindset focused on short-term gains. Instead, you adopt a strategic approach that values long-term relationships, leading to sustained profitability and a stronger position in the market.
Five Customer Value Management Transformations
Implementing CVM brings profound changes to how telecoms operate. This shift towards customer centricity leads to five key transformations that reshape the organization.
1. From a service-based to a whole-of-customer perspective:
Traditionally, telecoms analyze services like broadband, mobile plans, or digital offerings in isolation. This siloed perspective ignores how these services are used together and collectively shape the customer’s experience. Adopting a holistic view means understanding the entire customer journey, including all touchpoints, behaviors, and preferences. For example, a customer using both mobile and home internet services may value unified billing and integrated solutions that enhance satisfaction and strengthen loyalty across multiple services.
2. From revenue-based decisions to value and profitability-based decisions:
In a product-centric approach, decisions prioritize immediate revenue and conversions for specific products or offers. This approach can lead to multiple uncoordinated messages targeting the same customer, diminishing the customer experience (CX) and increasing churn risk. A shift to a value-driven approach involves considering the customer’s lifetime value and profitability metrics like CLV and margin. By integrating insights and aligning with customer needs, telecoms can foster sustainable long-term relationships. For example, offering personalized plan upgrades based on a customer’s usage pattern can increase ARPU while reducing churn.
3. From mass marketing campaigns to personalized, targeted marketing campaigns:
Historically, telecoms deployed mass-scale marketing campaigns aimed at reaching as many customers as possible. While such campaigns had broad reach, they were often expensive and resulted in generic messages with low engagement rates. The move towards a customer-centric approach involves shifting to highly targeted and personalized marketing campaigns, powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics. These campaigns are designed to deliver the right message through the most effective channel, whether via SMS, email, in-store, or social media. This approach ensures higher conversion rates and stronger engagement, reducing the cost of customer acquisition and improving overall campaign effectiveness.
4. From siloed to cross-functional and collaborative teams:
A customer-centric approach necessitates breaking down organizational silos to foster cross-functional teamwork. Collaboration between marketing, operations, customer service, and IT ensures that every team aligns with a shared customer-first strategy. For example, when launching a new service, coordinated efforts across departments can provide a seamless CX—from initial awareness to activation and beyond. This collaborative approach enables faster decision-making and more agile responses to customer needs.
5. From individual team goals to organization-wide strategic KPIs:
To become truly customer-centric, CVM helps to shift the organization’s focus from isolated performance metrics to strategic KPIs that measure the entire organization. These shared KPIs—such as net promoter score (NPS), churn reduction, and customer satisfaction—ensure that every team understands how their role in CX aligns with the customer and the organization’s goals. Aligning the teams towards shared objectives drives both accountability and collective success.
Transformation Enablers
Technology and data play a critical role in operationalizing these transformations. Modern CVM relies on integrating data, AI, and customer intelligence into campaign automation platforms. By harnessing vast datasets—from call records to social media activity—and applying machine learning (ML) models, telecoms have shifted from manual campaign targeting to real-time, personalized engagement.
These technologies enable dynamic interactions tailored to individual preferences and behaviors. For example, rules and predictive AI algorithms can trigger personalized offers based on a customer’s data usage or billing history, ensuring that each communication is relevant and timely.
CVM decisions are guided by four key types of advanced analytics:
- Descriptive analytics: Understanding past behaviors, such as service usage trends
- Predictive analytics: Forecasting future actions, like identifying customers likely to churn
- Preventive analytics: Anticipating risks to enable proactive interventions
- Prescriptive analytics: Recommending optimal actions based on predictive insights
These analytics, powered by AI and enriched with thousands of customer attributes, feed next best action (NBA) frameworks to identify the most optimal action to take with a customer at any given time. By delivering the right message at the right time through the appropriate channel, telecoms enhance CXs and build stronger relationships.
The impact of robust CVM strategies is profound. Telecom providers that embrace CVM report higher customer retention rates, increased CLV, and improved NPS. End-to-end automation enhances marketing efficiency by streamlining processes and enabling swift, accurate responses to customer needs.
Moreover, CVM frameworks equip telecoms to respond proactively to market challenges. During service disruptions, for example, CVM systems can prioritize high-value customers for immediate outreach, mitigating churn and preserving brand reputation. Continual learning from customer interactions ensures that engagement strategies evolve, delivering consistent results and sustaining a competitive edge.
In essence, CVM transforms telecoms by bridging the gap between traditional product-centric approaches and the modern need for customer-centric experiences. By placing the customer at the heart of every decision and leveraging technology to personalize interactions, telecoms can navigate the industry’s complexities and thrive in an era defined by change.
Previous: How to Use This Guide